First of all, there are many ways to interconnect devices on a LAN. But
the most popular for indoor cabling is by far the UTP cable.
As you can see in the picture bellow, this kind of cable got it's name from
the twisted pairs inside. UTP stands for Unshielded Twisted Pairs.
Here are the facts you should know about this widespread type of cable:
1. Conductors
UTP cable has 8 cooper conductors, isolated by a thin plastic cover. In
fact not all of these conductors are used for sending and receiving data.
Part of them (4) are used to diminish the "cross-talk" effect;
basically cross-talk refers to a noise generated by a metal conductor that
will interfere with one next to it. The 4 twisted pairs work like this: 4
conductors carry data, 4 carry the noise away from them.
2. Color coding
There are some cabling standards involved in implementing UTP-based
networks. All these are based on a color coding of the wires inside. The
colors are (no order here): Orange, Orange-White, Blue, Blue-White, Green,
Green-White, Brown and Brown-White.
3. Problems with UTP
UTP cable is highly susceptible to electromagnetic interferences (EMI).
This means that high voltage cables or electric motors can jam even block a
transmission.
If electromagnetic waves can get it, they can get out too. This means that
UTP cables offer only a maximum distance of 100 meters per cable of
guaranteed delivery due to signal attenuation. If you want to go more than
100 meters, you need to amplify the signal with something (switch, hub, etc).
This is why UTP suites better on indoor.
Use UTP cable outdoor only in safe places (no winds, heavy rain or snowing)
because it can break easily.
4. Cabling standards
There are two major cabling standards that you should be aware of:
a) TIA/EIA 568B, using this order:
PIN1: Orange - White
PIN2: Orange
PIN3: Green - White
PIN4: Blue
PIN5: Blue - White
PIN6: Green
PIN7: Brown - White
PIN8: Brown
b) TIA/EIA 568A, using this order:
PIN1: Green - White
PIN2: Green
PIN3: Orange - White
PIN4: Blue
PIN5: Blue - White
PIN6: Orange
PIN7: Brown - White
PIN8: Brown
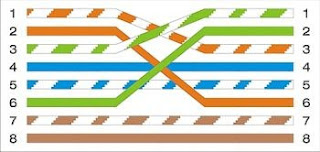
You can see an example bellow:
These connectors are called
RJ-45. They are similar to RJ-11 (telephone connectors), but have 8 pins
instead of 4.
5. Types of cables and their usage
Connections are standardized like this:
A. Straight-through cable (TIA/EIA 568B both ends of the cable)
- switch to PC
- switch to router
- between any other different devices
B. Crossover cable (TIA/EIA 568B at one end, TIA/EIA 568A at the other)
- switch to switch
- PC to PC
- router to router
- between any devices of the same type
C. Rollover cable (TIA/EIA 568B at one end, exactly the opposite of
TIA/EIA 568B at the other end)
- used to connect DB-9 to RJ-45 connectors to management consoles.
|





No comments:
Post a Comment